The client
City West Water (CWW, now Greater Western Water) were a water service provider supplying services to the City and Western City regions of Melbourne, Australia. A part-owned government entity, CWW were responsible for managing pipe network assets, pumping assets and wastewater treatment plants for the general public and many industrial customers. In December 2016 CWW launched its business strategy Customers First, Benefiting Communities with the vision of being an exceptional service provider.
The opportunity
In the 2021 budgeting process City West Water lacked clarity on how well capital and maintenance plans addressed the risk of failure across their asset portfolio. As a result there was a lot of concern about unaddressed condition of a number of asset classes and the potential loss that would result if this risk was left unmitigated. The capital budget for the year had essentially been set however it did not adequately address the condition of assets and the risk exposure to the business. A process was required that would quantify the financial risk associated with asset failure relative to CWW’s risk appetite.
How we helped
Our consultants assisted City West Water to use an already existing tool to demonstrate the financial risk associated with asset condition and pending asset failure. The Asset Risk Management Model (ARMM) was already a well established tool within CWW for assessing risk. The output from the ARMM was a quantified risk score that was typically accepted by government regulators (Budget allocators) and used as a guide to set budget.
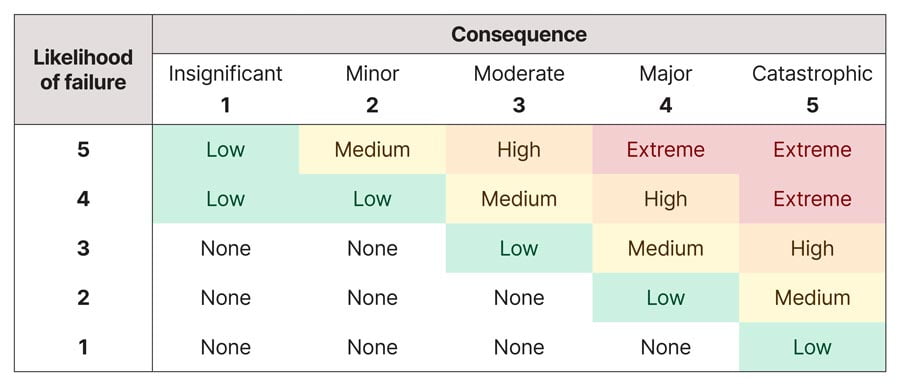
The risk score, based on consequence and likelihood was allocated across Economic, Social and Environmental risk. Our consultants helped to introduce the cost of repair risk (being the sum of the likely cost of repair, EPA fines and likely cost to property damage) and the probability of failure within the next 12 months to arrive at the financial risk of asset failure based on condition across the asset network. The financial risk of asset failure for assets without an allocated renewal plan was considered to be the residual risk of failure. This was then further categorized via a prioritization matrix based on likelihood.
“Assetivity helped CWW assess its current asset management approach and identify the key actions to improve our asset management maturity. Based on the insights provided we re-defined our organisational model for asset management, reviewed and updated our workforce capabilities and reset out asset management objectives. We have made significant steps to closer align our asset management approach with our customer expectations as a result of their work”
Sean Hanrahan, Service Planning Manager
Deliverables and benefits
City West Water were able to justify that there was $19.2M worth of risk that was not addressed by the 2021 capital budget funding for renewals. An additional $10M was allocated to renewals to address this residual risk. Further to identifying the residual risk in the 2021 capital budgeting cycle, CWW were able to show the amount of additional funding required over the next five years to reduce the residual risk of asset failure to within CWW’s accepted risk threshold.
Ready to get the best value from your assets?
If you wish to justify further investments in your assets and associate these with the financial or commercial risk to the business, we would be happy to support you. Browse our asset management consulting services below.
